Is Coconut Oil Good, or Bad for My Dog?
- August 31, 2023
- 4 mins 40 secs
With new studies recently released, is it time to rethink the use of coconut oil for our dogs? Coconut oil is a very popular product, used by pet owners all over the world, boasting some great health benefits. Take a look at the benefits, and some potential downsides of using coconut oil for your dogs with us!
When shopping for coconut oil, you may notice that both refined, and unrefined varieties are available. Unrefined coconut oil is the fresher option – this is the result of pressing fresh coconut flesh. Refined coconut oil is produced by pressing dried coconut flesh (called copra), so is more processed.
Virgin unrefined oils are typically the most pure option, as virgin oils are from the initial press, as opposed to subsequent presses, where non-virgin oils are produced, which are not as nutrient rich.
Coconut oil is rich in Medium-Chain Triglycerides (MCTs) – a type of saturated fat, healthier than heavy fats. Around 65% of coconut oil’s make up is MCTs! More on those later!
The MCT content of coconut oil has great antimicrobial properties, so can be used to help promote healing of minor wounds, pyoderma, and other fungal and bacterial skin issues. The specific fatty acid largely responsible for this is called Lauric Acid, which makes up around half of the MCTs.
Findings Here
Findings Here
Findings Here
The oil from coconuts is extremely moisturising to the skin! So moisturizing in fact, that studies comparing it to mineral oils (well renowned for being excellent for the skin) have been carried out! Results show coconut oil has just as much of a positive impact on skin moisture as mineral oil.
Findings Here
Let’s take a look at the benefits first, before we move on to the new research!
Those who feed coconut oil claim it helps their dog’s coat condition due to the content of fatty acids. People also notice a difference in dental health – coconut oil can be a great choice for a doggie toothpaste, mixed with a little bicarbonate of soda (baking soda for those reading from other parts of the world!).
Findings Here
There is some evidence to suggest that changes to cholesterol levels are possible by consuming coconut oil – it’s said to reduce the bad Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and increase the High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol in the body. There are also studies which state the very opposite, and that consuming coconut oil may actually increase levels of LDL. This conflict is something which needs further research, and is something to take into consideration if you’re looking at feeding it to your dog.
Findings Here
Coconut oil is antioxidant rich – this means it helps to combat dangerous free radicals in the body! Packing antioxidants into your dog’s diet is important, but other sources are available. Blueberries are one of the most powerful antioxidant sources readily available in your supermarket.
Findings Here
Seizure control is another proposed benefit to feeding coconut oil – this is because as part of a ketogenic diet, fats are important. There is evidence to suggest that the MCT content in coconut oil cause an increase in ketone levels in the bloodstream. There are links between high ketone concentrations and reduced frequency of seizures.
Findings Here
The new research findings affect the gut! As we always speak about here at My Pet Nutritionist; gut health is so incredibly important, and has a knock on effect to all parts of the body, as well as being largely responsible for immune health.
Leaky gut appears to be a major concern with feeding coconut oil, according to the new studies. Leaky gut happens when there is inflammation and irritation of the gut lining. The one-cell-thick intestinal lining is formed with ‘tight junctions’ in the healthy gut – this means the cells are right next to each other with no gaps, which stops particles from crossing the membrane into the bloodstream where they are recognised as foreign bodies, which presents symptomatically as intolerances. When irritated, gaps open up between the cells, which allows for particles to leak from the gut and into the bloodstream.
Studies show that the previously mentioned Lauric Acid, is inherently inflammatory. Studies also suggest that although antimicrobial, it may also destroy the membranes of lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which causes an immune response. The studies also state that coconut oil may cause the overproduction of LPS, and also increase it’s toxicity.
Findings Here
Findings Here
As coconut oil is a saturated fat, this also contributes to inflammation in the gut, which leads to leaky gut. The fat content of coconut oil is also a worry because high fat diets feed some bacteria, causing leaky gut.
Findings Here
For coat and skincare, internally, you can look at some other healthy fatty acid sources, such as fresh or tinned oily fish (sardines, mackerel), raw eggs, or algal oil. We have two fantastic blogs about feeding healthy fats to you dog!
Read more on omegas here.
Read more on raw eggs here.
This article should have given you an insight into the pros, and potential cons of using coconut oil, particularly internally, for your dog. We hope our balanced view gives you the knowledge you need to make in informed decision as to whether you give your dog coconut oil, or switch to an alternative. If you would like help improving your dog’s diet, or require help with a complex health issue, please don’t hesitate to book in for a consultation with one of our team.
Team MPN x
What is Coconut Oil?
Coconut oil is made by pressing the flesh of the coconut. The state of the flesh in its complete form, determines the type of oil produced.When shopping for coconut oil, you may notice that both refined, and unrefined varieties are available. Unrefined coconut oil is the fresher option – this is the result of pressing fresh coconut flesh. Refined coconut oil is produced by pressing dried coconut flesh (called copra), so is more processed.
Virgin unrefined oils are typically the most pure option, as virgin oils are from the initial press, as opposed to subsequent presses, where non-virgin oils are produced, which are not as nutrient rich.
Coconut oil is rich in Medium-Chain Triglycerides (MCTs) – a type of saturated fat, healthier than heavy fats. Around 65% of coconut oil’s make up is MCTs! More on those later!
Using Coconut Oil Externally
Coconut oil is often a fantastic choice for topical (external) use! It is used in the dog world for all sorts – flea prevention (as it makes the coat more slippery), to treat dry skin and noses, to soothe sore areas of skin, and much more!The MCT content of coconut oil has great antimicrobial properties, so can be used to help promote healing of minor wounds, pyoderma, and other fungal and bacterial skin issues. The specific fatty acid largely responsible for this is called Lauric Acid, which makes up around half of the MCTs.
Findings Here
Findings Here
Findings Here
The oil from coconuts is extremely moisturising to the skin! So moisturizing in fact, that studies comparing it to mineral oils (well renowned for being excellent for the skin) have been carried out! Results show coconut oil has just as much of a positive impact on skin moisture as mineral oil.
Findings Here
Using Coconut Oil Internally
Internal use of coconut oil is quite popular among the dog community, however, some new research suggests that it might not be such a good idea.Let’s take a look at the benefits first, before we move on to the new research!
Those who feed coconut oil claim it helps their dog’s coat condition due to the content of fatty acids. People also notice a difference in dental health – coconut oil can be a great choice for a doggie toothpaste, mixed with a little bicarbonate of soda (baking soda for those reading from other parts of the world!).
Findings Here
There is some evidence to suggest that changes to cholesterol levels are possible by consuming coconut oil – it’s said to reduce the bad Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and increase the High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol in the body. There are also studies which state the very opposite, and that consuming coconut oil may actually increase levels of LDL. This conflict is something which needs further research, and is something to take into consideration if you’re looking at feeding it to your dog.
Findings Here
Coconut oil is antioxidant rich – this means it helps to combat dangerous free radicals in the body! Packing antioxidants into your dog’s diet is important, but other sources are available. Blueberries are one of the most powerful antioxidant sources readily available in your supermarket.
Findings Here
Seizure control is another proposed benefit to feeding coconut oil – this is because as part of a ketogenic diet, fats are important. There is evidence to suggest that the MCT content in coconut oil cause an increase in ketone levels in the bloodstream. There are links between high ketone concentrations and reduced frequency of seizures.
Findings Here
What Does New Research Suggest?
As we mentioned, some new studies into the use of coconut oil internally, have been published! Of course, we had to read and digest them; so what do they say?The new research findings affect the gut! As we always speak about here at My Pet Nutritionist; gut health is so incredibly important, and has a knock on effect to all parts of the body, as well as being largely responsible for immune health.
Leaky gut appears to be a major concern with feeding coconut oil, according to the new studies. Leaky gut happens when there is inflammation and irritation of the gut lining. The one-cell-thick intestinal lining is formed with ‘tight junctions’ in the healthy gut – this means the cells are right next to each other with no gaps, which stops particles from crossing the membrane into the bloodstream where they are recognised as foreign bodies, which presents symptomatically as intolerances. When irritated, gaps open up between the cells, which allows for particles to leak from the gut and into the bloodstream.
Studies show that the previously mentioned Lauric Acid, is inherently inflammatory. Studies also suggest that although antimicrobial, it may also destroy the membranes of lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which causes an immune response. The studies also state that coconut oil may cause the overproduction of LPS, and also increase it’s toxicity.
Findings Here
Findings Here
As coconut oil is a saturated fat, this also contributes to inflammation in the gut, which leads to leaky gut. The fat content of coconut oil is also a worry because high fat diets feed some bacteria, causing leaky gut.
Findings Here
What can we use as an alternative?
As an alternative to coconut oil, for internal use, you may prefer to use a high quality MCT oil. It’s important to source a good MCT oil, as pure as possible, as not every MCT oil on the market is created equal!For coat and skincare, internally, you can look at some other healthy fatty acid sources, such as fresh or tinned oily fish (sardines, mackerel), raw eggs, or algal oil. We have two fantastic blogs about feeding healthy fats to you dog!
Read more on omegas here.
Read more on raw eggs here.
This article should have given you an insight into the pros, and potential cons of using coconut oil, particularly internally, for your dog. We hope our balanced view gives you the knowledge you need to make in informed decision as to whether you give your dog coconut oil, or switch to an alternative. If you would like help improving your dog’s diet, or require help with a complex health issue, please don’t hesitate to book in for a consultation with one of our team.
Team MPN x
Customer Reviews
Explore related products
Related articles

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
5 Reasons Why Your Dog May Have Diarrhoea
Jun 20 2024
•
5 mins 55 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
What is Pica, and Does Your Pet Have It?
May 23 2024
•
7 mins 15 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Pooh Guide for Dogs: What’s Good, and What’s Not
May 16 2024
•
9 mins 15 secs
Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Best Diet for Struvite Crystals in Dogs
Mar 13 2024
•
5 mins

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
All You Need to Know About Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency
Feb 22 2024
•
10 mins 20 secs
Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
What Causes Malabsorption in Dogs?
Feb 08 2024
•
7 mins 40 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
How to Support Liver Disease Naturally
Dec 21 2023
•
8 mins 30 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
How To Strengthen My Dog’s Immune System
Dec 07 2023
•
9 mins 15 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
The Ultimate Guide to Graves Disease in Pets
Nov 30 2023
•
11 mins

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
The Low Down on Furunculosis
Nov 09 2023
•
10 mins 45 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
The Lowdown on Lymphoplasmacytic Gastritis
Nov 02 2023
•
6 mins 45 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
How to Help My Yeasty Dog
Oct 26 2023
•
10 mins 30 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Can Food Sensitivities Cause a Pancreatic Flare?
Oct 20 2023
•
5 mins 40 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Why Does My Dog Have High Folate Levels?
Oct 12 2023
•
8 mins 10 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
What to Feed a Dog When Regurgitating
Sep 21 2023
•
4 mins 45 secs
Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Hotspots: What’s Causing Them, and How To Help
Sep 14 2023
•
6 mins 20 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
7 Reasons Why My Dog is Biting his Paws
Sep 06 2023
•
7 mins 40 secs
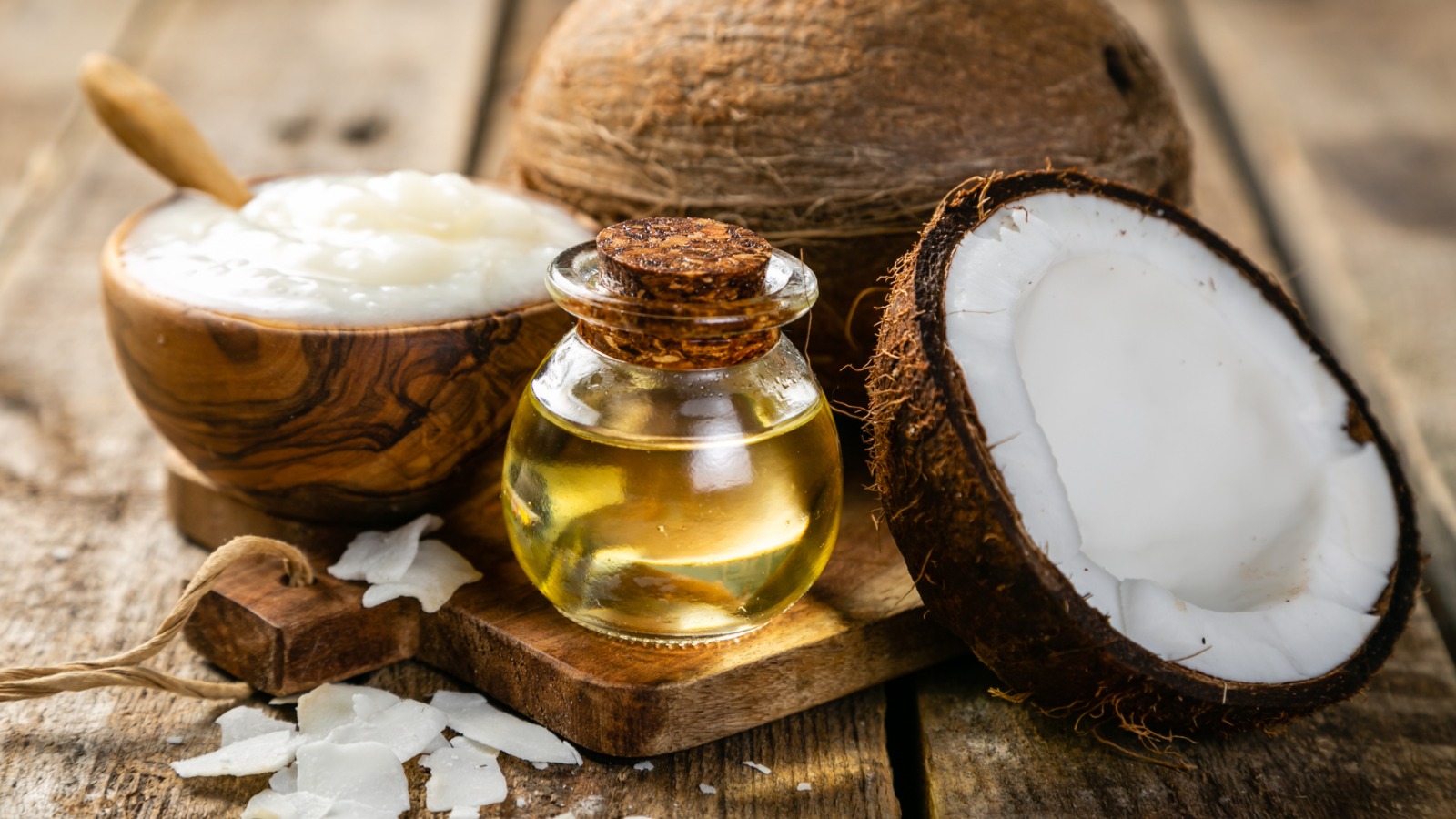

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Is Coconut Oil Good, or Bad for My Dog?
Aug 31 2023
•
4 mins 40 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
What Should I Feed My Dog with Acid Reflux?
Jul 26 2023
•
4 mins 15 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Gallstones, and Why Your Dog Has Them
Jun 22 2023
•
6 mins 40 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
5 Cornerstones of Immunity for your Pet
Jun 15 2023
•
6 mins

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
7 Factors Affecting Immunity
Feb 27 2023
•
8 mins 30 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
The Link Between Leaky Gut and Arthritis
Jan 31 2023
•
9 mins 40 secs
Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
The Connection Between Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity – Part 2
Jan 18 2023
•
7 mins 30 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
The Connection Between Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity – Part 1
Jan 18 2023
•
4 mins

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
11 Signs Your Pet Has Low Stomach Acid
Jan 04 2023
•
6 mins 30 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
5 Reasons for Alopecia in Pets
Nov 16 2022
•
4 mins 30 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
How Can I Use Food To Support My Anxious Dog?
Nov 01 2022
•
3 mins 40 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
How Does The Gut Influence My Pet’s Immune Health
Aug 23 2022
•
4 mins

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Support Your Pet’s Gut Health with the 4 R’s
Aug 22 2022
•
4 mins

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
8 Reasons For Your Dog’s Licking Behaviour
Aug 02 2022
•
7 mins 20 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Things To Think About: Skin Health in Dogs
Aug 01 2022
•
7 mins 30 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Does My Dog Have an Allergy or an Intolerance?
May 10 2022
•
4 mins 42 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
5 Tips to Support Your Seasonally Itchy Dog
Apr 26 2022
•
4 mins 50 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Why Do Allergies in Dogs Develop?
Apr 21 2022
•
5 mins 36 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
4 Tips to Support Your Dog with IBS
Apr 19 2022
•
3 mins 45 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Does My Dog Have a Gut-Brain Axis?
Mar 28 2022
•
6 mins 7 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
7 Foods That Add Fibre To Your Dog’s Diet
Mar 21 2022
•
5 mins 2 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
3 Top Tips For Anal Gland Health in Dogs
Mar 21 2022
•
4 mins 23 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
A Brief Guide to Our Pet’s Pancreas
Mar 07 2022
•
6 mins 24 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Why Does My Dog Need Vitamins? Part Two – The Water-Soluble Vitamins
Jan 24 2022
•
6 mins 42 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Why Does My Dog Need Vitamins? Part One – The Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Jan 24 2022
•
5 mins 51 secs
Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Prebiotics Vs. Probiotics
Nov 01 2021
•
4 mins 17 secs

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
To Fast Or Not To Fast? That Is The Question
Aug 23 2021
•
5 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Keeping Your Senior Dog Healthy
Aug 17 2021
•
5 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Bacterial Overgrowth – More Common Than You Think
Aug 04 2021
•
6 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
My Pet Eats Grass, Should I be Worried?
Jul 27 2021
•
5 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Can Stress Affect My Dog’s Digestive System?
Jul 26 2021
•
8 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
What Can Go Wrong with My Dog’s Gallbladder?
Jul 21 2021
•
5 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
A Brief Guide to Histamine Intolerance for Dogs
Jul 13 2021
•
4 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
What Can Cause Gut Dysbiosis?
Jun 21 2021
•
7 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
What Can Help Gut Dysbiosis?
Jun 21 2021
•
9 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Why Is My Dog Regurgitating?
Jun 07 2021
•
5 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Why is My Dog Licking His Lips?
May 25 2021
•
5 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
The Importance of Nature for Human and Dog Health
May 12 2021
•
5 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
How Food Affects Your Dog’s Behaviour
Apr 22 2021
•
10 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Lectins and Should My Dog Eat Them?
Apr 12 2021
•
6 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Low Histamine Diets, Why and When!
Apr 07 2021
•
7 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Constipation in Cats and Dogs!
Feb 22 2021
•
8 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Why Is My Dog A Fussy Eater?
Jan 18 2021
•
10 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Why Does My Dog Keep Licking?
Jan 11 2021
•
9 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
5 Reasons Why Your Dog May Have Diarrhoea
Jan 07 2021
•
6 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Why is My Dog Losing His Hair?
Jan 04 2021
•
7 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Tackling Atopic Dermatitis in Pets
Dec 16 2020
•
9 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
5 Top Tips for Skin Health in Your Dog
Dec 08 2020
•
9 min read
Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
5 Reasons Why Fibre is Your Dog’s Best Friend
Oct 28 2020
•
7 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Why Probiotics Are Good For You And Your Dog
Oct 20 2020
•
8 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Do Dogs Need Carbohydrates?
Aug 31 2020
•
10 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Natural Worming Options for Pets
Jun 03 2020
•
8 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
The Ultimate Natural UT Guide for Pets
Apr 14 2020
•
9 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Natural Guide for Pets: Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Apr 06 2020
•
8 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Natural Guide for Acid Reflux in Dogs
Mar 31 2020
•
8 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
The 4 Corner Stones for Healthy Anal Glands, Naturally
Mar 27 2020
•
10 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
7 Steps to Optimal Gut Health for Pets
Mar 13 2020
•
8 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
7 Top Reasons to use Clay in your Dog’s Diet Regime
Feb 20 2020
•
5 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Itching has become such an epidemic
Feb 18 2020
•
6 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
An itch you just can’t scratch!
Feb 12 2020
•
3 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
Itchy cats and dogs naturally!
Jan 23 2020
•
7 min read

Dietary NeedsGeneral HealthGut Health
5 reasons why your dog eats grass
Feb 21 2019
•
2 min read
✕